Breastfeeding/Formula Feeding
What Makes a High Calorie Feeding Tube Formula Effective?
A deep dive into the factors behind effective high-calorie feeding tube formulas will change how you view nutritional support in hospitals.
When examining the components that contribute to an effective high-calorie tube feeding formula, it’s fascinating to note that nearly one-fourth of patients in hospitals might need support with enteral nutrition during their hospitalization.
But what exactly contributes to the effectiveness of these specialized formulas? The answer lies in a complex interplay of factors, from the nutrient content and digestibility to the caloric density and customization of the formula.
Join us as we uncover the key elements that guarantee these high-calorie feeding tube formulas truly meet the nutritional needs of patients in a profound way.
Key Takeaways
- Premium ingredients, like hydrolyzed collagen and MCTs, enhance nutrient absorption for critically ill patients.
- Customization addresses specific nutritional needs, aiding in combating deficiencies and improving outcomes.
- Balancing caloric density optimizes energy provision while minimizing risks like overfeeding and GI discomfort.
- Diverse fatty acid profiles, such as omega-3 and omega-6, support health, inflammation reduction, and heart function.
Nutrient Content Considerations
When considering nutrient content in high calorie feeding tube formulas, it's essential to focus on the concentrated macronutrients and micronutrients provided to meet specific nutritional needs.
Fatty acids, a critical component of these formulas, play a vital role in energy provision and overall health. High calorie formulas often contain a blend of saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fats to support various bodily functions.
Polyunsaturated fatty acids, such as omega-3 and omega-6, are particularly beneficial for reducing inflammation and supporting heart health. These essential fatty acids are necessary for proper cell function and can't be produced by the body, emphasizing their importance in high calorie feeding tube formulas.
By including a diverse range of fatty acids in these formulas, healthcare providers can ensure that patients receive well-rounded nutrition that supports their unique dietary requirements.
It's crucial to consider the types and amounts of fatty acids present in high calorie formulas to optimize patient outcomes and promote overall well-being.
Digestibility Factors to Consider
Considering the digestibility factors in high calorie feeding tube formulas is paramount for ensuring efficient nutrient absorption and supporting overall patient well-being. When evaluating the digestibility of these formulas, several key factors should be taken into account:
- Inclusion of Medium-Chain Triglycerides (MCTs): MCTs are easily digestible fats that provide a quick source of energy for patients, especially those with gastrointestinal issues that may compromise fat absorption.
- Hydrolyzed Collagen Content: The presence of hydrolyzed collagen aids in digestion and absorption of essential amino acids, important for protein synthesis and tissue repair.
- Utilization of Whey Protein: Whey protein, known for its high-quality amino acid profile, supports easy digestion and utilization by the body, promoting muscle growth and overall recovery.
- Enhanced Nutrient Absorption: Effective high calorie formulas are formulated to promote best nutrient absorption in patients with compromised gastrointestinal function, ensuring that patients receive the necessary nutrients for their well-being and recovery.
Importance of Ingredient Quality
Optimizing the quality of ingredients in high-calorie feeding tube formulas is essential for maximizing nutrient absorption and supporting diverse patient needs, particularly critically ill patients. The ingredients used greatly impact the digestibility, tolerance, and overall effectiveness of the formula in meeting the nutritional requirements of these patients. For critically ill individuals, whose nutrient needs are often elevated due to their condition, high-quality ingredients play a crucial role in ensuring that the body can efficiently utilize the nutrients provided.
Premium ingredients such as hydrolyzed collagen, medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), and whey protein not only enhance the nutritional profile of the formula but also contribute to better patient outcomes. The sourcing and composition of these ingredients are critical factors that influence the formula's efficacy in delivering essential nutrients to individuals who may have compromised digestive systems or increased nutrient demands. By prioritizing ingredient quality, healthcare providers can better support the unique nutritional needs of critically ill patients through high-calorie feeding tube formulas.
Role of Caloric Density

Increasing the caloric density of feeding tube formulas is essential for providing enhanced energy delivery in a more concentrated form to meet the nutritional requirements of patients with limited gastrointestinal capacity. When considering the role of caloric density in high-calorie feeding tube formulas, there are both pros and cons to keep in mind:
- Pros:
- More Energy in Smaller Volume: Higher caloric density allows for increased energy provision without the need for large volumes, which can benefit patients with restricted fluid intake.
- Meeting Nutrient Needs: Caloric density plays a critical role in ensuring that patients receive essential nutrients even with limited intake capacity.
- Cons:
- Risk of Overfeeding: The concentrated nature of high-calorie formulas may pose a risk of overfeeding if not carefully monitored.
- Potential for GI Distress: Some patients may experience gastrointestinal discomfort or intolerance to highly concentrated formulas.
Balancing these factors is vital in optimizing feeding tube formulas to meet the specific needs of each patient effectively.
Impact of Formula Customization
When customizing high-calorie feeding tube formulas, healthcare providers can tailor nutritional content to meet the specific needs of individual patients, optimizing their recovery and overall health.
This customization is important as it allows for adjustments that address possible causes of malnutrition, such as unique dietary restrictions, preferences, or metabolic demands. By fine-tuning the calorie and protein content, specialized formulas can effectively combat specific nutrient deficiencies in critically ill patients.
For instance, patients with conditions like diabetes may require formulas that are lower in simple sugars but higher in healthy fats to manage blood sugar levels effectively. Additionally, individuals with digestive disorders might benefit from formulas that are easier to digest, reducing the likelihood of gastrointestinal discomfort.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do You Increase Calories in Tube Feeding?
We increase calories in tube feeding by using high-calorie formulas tailored for enteral nutrition therapy. These formulas offer concentrated nutrition to support patients needing extra caloric intake.
By adjusting the caloric density of the formulas, we can meet the energy needs of patients with higher calorie requirements.
This approach is vital for addressing malnutrition and aiding patients with limited oral intake.
What Is Calorie Dense Tube Feeding Formula?
Calorie dense tube feeding formulas pack more energy into less liquid volume, ideal for patients needing high caloric intake or those with limited feeding capacity. These formulas efficiently deliver essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals to support patients' nutritional needs.
When choosing a formula, consider individual requirements, medical conditions, and dietary goals. How can these formulas benefit patients with different needs and conditions?
How Many Calories Can You Eat in a Feeding Tube?
We can adjust the caloric intake from a feeding tube based on individual needs and goals. The amount can range from 1,200 to 2,000 calories per day.
Tailoring feeding tube formulas to deliver specific calorie amounts is essential for meeting nutritional requirements. Higher calorie formulas are particularly beneficial for patients with increased energy needs.
The caloric content of these formulas plays a critical role in supporting patients who can't eat orally.
How Do You Determine Calorie and Protein Needs for the Tube Feeding Patient?
When determining calorie and protein needs for tube feeding patients, we consider factors like age, weight, activity level, and medical condition. Protein requirements can vary from 1.0 to 2.0 grams per kilogram of body weight per day.
Accurate calculations are essential to prevent malnutrition and promote healing. Collaboration with a healthcare provider or dietitian helps set personalized goals for best nutrition support.
Conclusion
To sum up, finding the right high-calorie feeding tube formula is vital for supporting a patient's nutritional needs. By considering nutrient content, digestibility, ingredient quality, caloric density, and customization, healthcare providers can tailor a formula to optimize outcomes.
Remember, it's not just about the calories, but the quality and balance of nutrients that make all the difference in the patient's health and well-being. So, let's make sure we choose the formula that's the whole enchilada for our patients' nutritional requirements.
With over a decade of experience in editorial leadership, Esther has been at the helm of Mother Baby Kids since its inception. Her journey into parenting content was inspired by her own experiences as a mother, navigating the joys and challenges with a desire to support other parents. Esther is passionate about storytelling that connects, educates, and empowers families from all walks of life.
Breastfeeding/Formula Feeding
Managing Reflux: Breastfeeding Diet Tips
Balancing your breastfeeding diet with reflux in mind can make a world of difference for your baby – discover how in our essential guide.

When it comes to managing reflux, we all know how challenging it can be to navigate the world of breastfeeding and dietary adjustments. But fear not, as we have some valuable tips to help ease your baby's discomfort and support their digestive health.
From simple dietary tweaks to understanding the impact of your food choices, our practical advice will empower you to make informed decisions for both you and your little one. Whether you're a new mom or a seasoned pro, these insights could be just what you need to find relief and nurture your baby's well-being.
Key Takeaways
- High fiber foods aid digestion for reflux management.
- Avoid trigger foods like cow's milk and soy to reduce symptoms.
- Thicken breast milk with rice cereal for easier digestion.
- Maintain a food diary to track triggers and symptoms accurately.
Foods to Include in Breastfeeding Diet for Reflux
When managing reflux through a breastfeeding diet, including foods high in fiber, lean proteins, probiotics, Omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants can help alleviate symptoms and promote digestive health.
For breastfed babies experiencing reflux, pondering the impact of a mother's diet on their digestive system is crucial. Fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains aid in digestion, reducing the likelihood of reflux episodes.
Lean proteins such as chicken, turkey, and fish support muscle function, contributing to overall health for both mother and baby. Probiotic-rich foods like yogurt and kefir can help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria in babies, potentially reducing reflux symptoms.
Additionally, incorporating Omega-3 fatty acids from sources like salmon and walnuts can help decrease inflammation, which may alleviate discomfort associated with reflux in breastfed infants. Antioxidant-rich foods like berries, spinach, and nuts can support the immune system, providing added benefits for both mother and baby through breast milk.
Impact of Maternal Diet on Baby's Reflux

Maternal dietary choices play a significant role in influencing a breastfed baby's experience with reflux, as allergens passed through breast milk can impact the occurrence and severity of reflux symptoms. When considering how your diet affects your baby's reflux, it's crucial to be mindful of what you consume.
Here are some practical tips to help manage your baby's gastroesophageal reflux:
- Avoid Trigger Foods: Certain foods like cow's milk and soy can exacerbate reflux symptoms in breastfed babies.
- Limit Acidic, Spicy, and Fatty Foods: Steering clear of these types of foods can help reduce the likelihood of reflux in your little one.
- Thicken Breast Milk: Adding rice cereal to breast milk can help thicken it, potentially easing reflux symptoms for your baby.
- Keep a Food Diary: Tracking what you eat and your baby's reflux symptoms can help you identify specific triggers in your diet that affect your baby.
- Consult a Healthcare Provider: If you're unsure about which dietary changes to make, consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice on managing your baby's reflux through your diet.
Dietary Strategies for Managing Reflux Symptoms
To effectively manage reflux symptoms in breastfed babies, it's essential to implement dietary strategies that focus on avoiding trigger foods and promoting easier digestion. When breastfeeding a baby with reflux, it's recommended to thicken breast milk with rice cereal to help reduce episodes of reflux. Additionally, it's advised to steer clear of acidic fruits, tomatoes, spicy foods, and high-fat foods in your diet as these can exacerbate reflux symptoms in your baby. Opting for smaller, more frequent feeds and ensuring your baby stays upright after feedings can also aid in minimizing reflux episodes.
Considering the impact of cow's milk on reflux in breastfed babies is important. Some babies may be sensitive to cow's milk proteins transferred through breast milk, leading to increased reflux symptoms. Consulting with a healthcare provider to explore the possibility of eliminating cow's milk from your diet can be beneficial in managing your baby's reflux. By maintaining a food and symptom diary, you can track any patterns and identify specific triggers that may be causing discomfort for your baby.
Best Practices for Breastfeeding Moms With Reflux Babies

Breastfeeding moms of babies with reflux can benefit from implementing best practices that focus on identifying triggers, promoting comfort, and optimizing feeding techniques. When dealing with reflux disease in breastfed babies, it's crucial to create a supportive environment that aids in managing their symptoms effectively. Here are some best practices to take into account:
- Maintain a Food and Symptom Diary: Tracking what you eat and your baby's reactions can help pinpoint potential triggers for reflux episodes.
- Eliminate Common Allergens: Removing cow's milk and soy from your diet may alleviate reflux symptoms in your breastfed baby.
- Ensure a Good Latch: A proper latch and minimizing air intake during feedings can reduce discomfort for babies with reflux.
- Implement Elimination Diets: Gradually reintroducing foods can help identify and manage any food intolerances your baby may have.
- Opt for Frequent Feedings: Offering smaller, more frequent feedings can help prevent overfeeding and reduce the likelihood of reflux episodes.
Holistic Nutrition Approaches for Reflux Management
When managing reflux in breastfeeding infants, incorporating holistic nutrition approaches can greatly impact symptom reduction and overall well-being. Baby Reflux Lady, it's vital to focus on whole, unprocessed, and organic foods to prevent acid reflux in babies. By following elimination diets, we can identify trigger foods causing our baby's reflux, ultimately reducing episodes of reflux and minimizing our baby's pain. It's important to keep our baby upright after feedings to help prevent the regurgitation of stomach contents, which can worsen reflux symptoms. Holistic nutrition emphasizes nutrient-dense foods that promote ideal health for both mother and baby, steering clear of processed and refined foods known to trigger acid reflux in infants. By understanding and implementing holistic nutrition practices, we can support our baby's digestive health and well-being effectively.
| Holistic Nutrition Approaches | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Focus on whole, unprocessed, organic foods | Prevents acid reflux |
| Utilize elimination diets to identify trigger foods | Reduces reflux episodes |
| Keep baby upright after feedings | Minimizes regurgitation of stomach contents |
Frequently Asked Questions
What Foods Should Breastfeeding Moms Avoid With Reflux?
We should avoid acidic fruits like apples and oranges, tomatoes, spicy foods, caffeine, and fatty foods when breastfeeding babies with reflux. These can worsen symptoms. Let's stick to reflux-friendly options to help our little ones feel better.
How Do I Feed My Breastfed Baby With Acid Reflux?
We feed our breastfed baby with acid reflux in an upright position to reduce regurgitation, consider smaller, more frequent feedings, thicken breast milk with rice cereal, burp frequently, and avoid acidic, spicy, and high-fat foods in our diet to help ease symptoms.
What Makes Reflux Worse in Breastfed Babies?
Overfeeding, rapid feeding, trigger foods like dairy or caffeine, poor latch, bad positioning, maternal stress, and inconsistent feeding schedules contribute to worsening reflux in breastfed babies. Being mindful of these factors can help manage reflux symptoms effectively.
What Can I Eat to Reduce Baby Reflux?
We can eat non-acidic fruits like bananas and melons, lean proteins such as chicken and fish, whole grains like brown rice and oats, and vegetables like spinach, broccoli, and carrots to help reduce baby reflux.
Conclusion
Just like a gardener tends to their garden with care, breastfeeding moms can nurture their babies by managing reflux with a balanced diet. By planting the right foods and avoiding common triggers, moms can help their little ones thrive and grow without the discomfort of reflux.
Remember, just as a well-tended garden blossoms beautifully, a well-nourished baby can flourish and thrive with the right dietary support. So, let's keep feeding our babies with love and care, one meal at a time.
With a rich background in writing and a keen interest in child development, she specializes in creating insightful, compassionate content that speaks directly to parents’ concerns and aspirations. Margaret believes in the power of shared experiences to bring comfort and confidence to parents everywhere.
Breastfeeding/Formula Feeding
Anti-Colic Diet for Breastfeeding Mothers: A How-To Guide
A transformative guide to an anti-colic diet for breastfeeding mothers – discover the secret to a calmer, happier baby.

When exploring the realm of managing colic in infants, one can’t help but wonder about the impact of their diet on their little one’s comfort. We’ve all heard anecdotes of certain foods causing tummy troubles for babies, but what if a simple dietary tweak could make a world of difference?
Imagine a world where fussy feedings become a thing of the past, and both mother and baby can enjoy a more peaceful bonding experience. Let’s explore the potential of an anti-colic diet for breastfeeding mothers and how it might just be the key to a calmer, happier baby.
Key Takeaways
- Exclude common trigger foods like dairy and caffeine to prevent colic symptoms.
- Incorporate soothing ingredients like ginger and fennel for digestive relief.
- Be mindful of allergens in breast milk by avoiding potential irritants.
- Consider enzyme supplementation to aid in the digestibility of breast milk and reduce colic.
Common Trigger Foods for Colic
When considering an anti-colic diet for breastfeeding mothers, it’s essential to be aware of common trigger foods that can exacerbate colic symptoms in infants. Dairy products, such as cow’s milk, are known to cause allergic reactions in some breastfed babies, leading to colic issues.
High caffeine intake, commonly found in coffee, tea, and chocolate, can also contribute to colic symptoms in infants. Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cabbage are potential culprits for gas and colic in breastfed babies due to their tendency to produce gas.
Additionally, spicy or highly seasoned foods may cause sensitivity in some infants, further aggravating colic symptoms. It’s important for breastfeeding mothers to be cautious of potential food allergies, particularly to nuts and peanuts, as these can trigger colic in their babies.
Being mindful of these common trigger foods can help alleviate colic symptoms and promote a more comfortable feeding experience for both mothers and infants.
Incorporating Soothing Ingredients Into Meals

Incorporating soothing ingredients like ginger, fennel, and chamomile into meals can effectively alleviate colic symptoms in breastfed babies. When preparing meals to help soothe your baby, consider the following:
- Ginger: Known for aiding digestion and reducing gas, ginger can be beneficial in easing colic symptoms in infants by promoting better digestion and alleviating discomfort.
- Fennel: This herb not only adds a pleasant flavor to dishes but can also help ease stomach discomfort and bloating in babies suffering from colic, providing relief for their digestive system.
- Chamomile: With its calming properties, chamomile may help relax a colicky baby’s digestive system and reduce fussiness, offering a gentle and natural approach to soothing your little one.
- Natural Relief: By incorporating these soothing ingredients into your meals, you can provide natural relief for both you and your baby, embracing a holistic approach to managing colic through diet. These ingredients are safe for consumption and can contribute to a more comfortable feeding experience for your baby.
Understanding the Breastfeeding-Colic Connection
The relationship between breastfeeding and colic in infants is influenced by various factors, including substances present in a mother’s breast milk. Breastfed babies may experience colic symptoms due to allergenic foods or irritants passed through breast milk from the mother’s diet. Since infants have an underdeveloped digestive system, certain foods can cause colic by triggering sensitivity or irritation.
To reduce colic symptoms in breastfed babies, mothers can avoid consuming potential culprits such as dairy, caffeine, spicy foods, and gas-inducing vegetables. Monitoring the mother’s diet is important as breast milk contains enzymes like amylase and lipase that aid in digestion. By being mindful of what they eat, mothers can help prevent infantile colic and promote a more comfortable feeding experience for their babies.
Understanding the breastfeeding-colic connection empowers mothers to make informed choices that support their child’s well-being.
The Role of Digestive Enzymes in Colic Relief

Understanding how digestive enzymes play an important role in colic relief for both breastfeeding mothers and their babies is essential in managing infantile colic symptoms.
- Natural Enzymes in Breast Milk: Breast milk contains digestive enzymes like amylase and lipase, aiding in the digestion process for babies.
- Plant-Based Enzymes Support: Fruits such as papaya, pineapple, and kiwi are rich in plant-based enzymes that can support digestion and help reduce colic symptoms in infants.
- Enzyme Supplementation Benefits: Supplementing with enzymes can make sure that nutrients are easily digestible for babies, potentially reducing colic triggers.
- Preventing Irritant Transfer: Enzymes can help prevent the transfer of irritants from a mother’s diet through breast milk to her nursing baby, hence minimizing the likelihood of colic episodes.
Implementing an Anti-Colic Diet Plan
For breastfeeding mothers looking to alleviate colic symptoms in their babies, crafting an anti-colic diet plan is an important step towards providing relief and comfort for both mother and child. To reduce colic in breastfed babies, it’s vital to identify common allergens like cow’s milk proteins, eggs, wheat, peanuts, tree nuts, and soy, and exclude them from your breastfeeding diet.
Additionally, avoiding gluten-containing grains such as wheat, oats, barley, and rye can help lower the likelihood of colic episodes. Limiting intake of foods like garlic, onions, cabbage, turnips, broccoli, and beans is important as they can impact breast milk and potentially trigger colic in your little one.
Cutting out caffeinated drinks like tea and coffee is recommended to prevent discomfort in your baby and minimize colic symptoms. Be cautious with specific fruits like apricots, rhubarb, prunes, melons, and peaches, as they may lead to colic flare-ups due to wind sensitivity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Should Breastfeeding Mothers Eat to Prevent Colic?
We eat foods that avoid allergens like cow’s milk, eggs, wheat, peanuts, and soy to help prevent colic in breastfed babies. Steering clear of gluten grains, garlic, onions, caffeine, and certain fruits can also aid in reducing colic symptoms for infants.
What Foods Are Anti-Colic for Breastfeeding?
We focus on anti-colic foods for breastfeeding mothers – lean proteins for easy digestion, probiotic-rich choices for a healthy gut, dark leafy greens for nutrients, whole grains for energy, and Omega-3s for brain development.
How Can I Prevent My Breastfed Baby From Getting Colic?
We can prevent our breastfed baby from getting colic by monitoring our diet, offering a pacifier for comfort, holding and soothing them, trying different feeding positions, and burping them regularly. These steps can help reduce colic symptoms.
What Is the Best Way to Feed My Baby to Avoid Colic?
We found that adjusting our feeding routine, like trying different positions and being mindful of our diet, helped ease our baby’s colic. It’s tough, but staying patient and seeking support from loved ones can make a difference.
Conclusion
In the symphony of motherhood, our diet serves as the conductor, guiding our little ones towards a harmonious feeding experience.
By tuning into our bodies and making mindful food choices, we can create a soothing melody that alleviates colic in our breastfeeding babies.
Let our meals be a symphony of comfort and relief, nourishing both mother and child in perfect harmony.
With a rich background in writing and a keen interest in child development, she specializes in creating insightful, compassionate content that speaks directly to parents’ concerns and aspirations. Margaret believes in the power of shared experiences to bring comfort and confidence to parents everywhere.
Breastfeeding/Formula Feeding
Breastfeeding Safe Diet: 10 Foods for a Healthy Mom and Baby
Optimize your breastfeeding journey with these 10 essential foods rich in nutrients for both you and your baby, ensuring a healthy start together.

When considering a breastfeeding safe diet, one might worry about the time and effort involved in planning meals. However, with our list of 10 foods for a healthy mom and baby, you'll discover simple and nourishing options that can easily fit into your routine.
From whole grains to hydrating essential components, each food item plays an important role in supporting your well-being and providing essential nutrients for your little one.
So, let's explore these dietary choices that can make a significant difference in your breastfeeding journey.
Key Takeaways
- Incorporate whole grains, lean proteins, and colorful fruits for optimal nutrition during breastfeeding.
- Include legumes, healthy fats, and hydrating foods to support postpartum health and milk production.
- Monitor hydration levels by observing urine color and drink water regularly to aid breastfeeding and overall well-being.
- Focus on nutrient-dense foods like salmon, leafy greens, and nuts for brain development and energy during lactation.
Whole Grains
When incorporating whole grains into a breastfeeding-safe diet, opt for nutrient-dense choices like brown rice, whole-wheat pasta, and oatmeal to support both maternal health and milk production. Whole grains are rich in iron, an important nutrient during breastfeeding to prevent fatigue and support overall well-being.
Additionally, the fiber content in whole grains aids in digestion, which is essential for postpartum recovery. These complex carbs not only keep you feeling full longer but also provide sustained energy important for the demands of breastfeeding.
Including whole grains in your meals can help boost milk production and make sure that you have the necessary nutrients to support your baby's growth and development. By choosing whole grains over refined grains, you're making a healthier choice that benefits both you and your little one.
Whether it's a warm bowl of oatmeal for breakfast or whole-wheat pasta for dinner, these nutrient-packed grains are a versatile and nutritious addition to your breastfeeding diet.
Salmon and Sardines
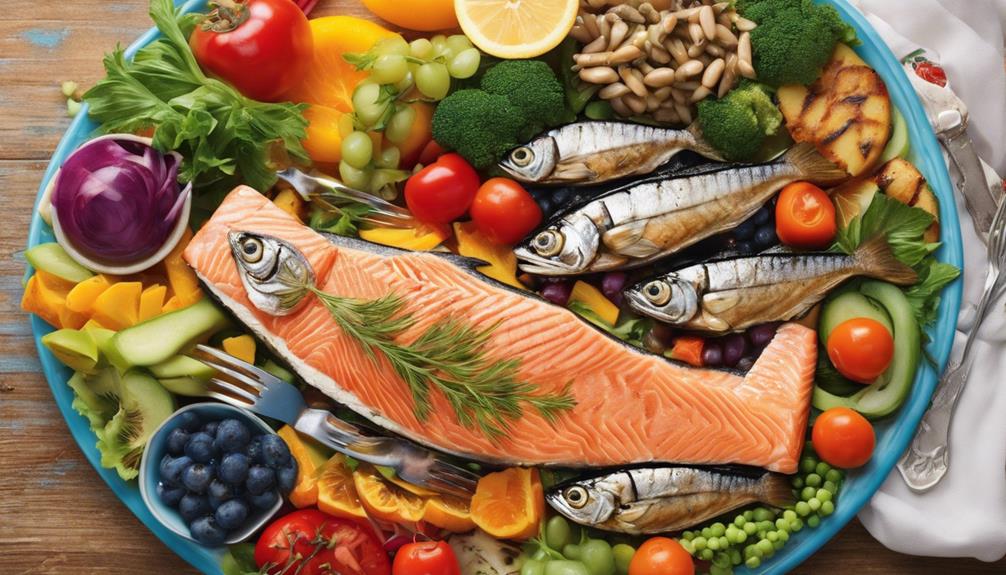

Incorporating salmon and sardines into a breastfeeding-safe diet provides essential nutrients for both maternal health and infant development. These fatty fish aren't only rich sources of protein, important for energy and muscle repair during breastfeeding, but they also contain omega-3 fatty acids, such as DHA, essential for infant brain development. The omega-3 DHA found in salmon and sardines plays a key role in supporting the baby's nervous system, skin, and eye health.
Including salmon and sardines in the diet can enhance the quality of breast milk by increasing DHA levels, which is beneficial for the baby's growth and overall health. The nutrients present in these fish make them valuable additions to a breastfeeding mother's diet, ensuring essential nutrition for both herself and her baby. By enjoying salmon and sardines regularly, mothers can provide essential nutrients that support their well-being and their infant's development.
Leafy Green Vegetables
How do leafy green vegetables contribute to the essential nutrition needed for breastfeeding mothers and their babies? Leafy greens, such as spinach and kale, play a critical role in providing the vitamins and minerals necessary for both mom and baby during the breastfeeding period. Here are some key benefits of incorporating leafy greens into your diet:
- Vitamins Galore: Leafy green vegetables are packed with vitamins A, C, E, and K, offering a diverse range of essential nutrients important for overall health and immunity.
- Iron Boost: Iron-rich options like spinach help maintain energy levels and prevent deficiencies that can occur while breastfeeding, supporting maternal well-being.
- Bone Health Support: Calcium-rich leafy greens such as broccoli and Swiss chard contribute to bone health, benefiting both the mother and the developing baby.
Including a variety of leafy greens in your meals ensures a well-rounded intake of nutrients that are important for optimal health and well-being while breastfeeding.
Lean Protein Sources

Leafy green vegetables offer a plethora of nutrients important for breastfeeding mothers and their babies, and now we shift our focus to the importance of incorporating lean protein sources into their diet. Lean protein sources such as chicken and turkey play an essential role in providing essential amino acids necessary for muscle repair and energy levels. These meats are also rich in iron, which is important for both mother and baby during the breastfeeding period.
Including chicken and turkey in your diet can help meet the increased protein demands of lactation while keeping the calorie intake in check. These lean meats are versatile and can be prepared in various ways, making them convenient for busy breastfeeding moms. Opting for skinless poultry cuts and cooking methods that involve minimal added fats can further enhance their nutritional profile.
Colorful Fruits
Colorful fruits like berries, oranges, and kiwi offer a wealth of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants important for breastfeeding mothers and their babies. These fruits provide hydration, fiber, and natural sugars to boost energy levels during lactation.
- Berries: Low in calories but high in nutrients like vitamin C, supporting the immune system.
- Oranges: Good source of vitamin C, folate, and fiber, aiding in digestion and overall health.
- Kiwi: Packed with vitamin K, vitamin E, and potassium, promoting heart health and bone strength for both mother and baby.
Including these colorful fruits in your diet not only enhances your nutrient intake but also adds a burst of flavor to your meals. Whether enjoyed as a snack, added to smoothies, or incorporated into salads, these fruits can help meet your daily vitamin needs while keeping you feeling refreshed and energized throughout the day. Prioritizing these foods can contribute to a well-rounded diet that supports both you and your baby during the breastfeeding journey.
Dairy Products

Moving from the discussion on colorful fruits to the topic of dairy products, it's important to highlight their significant role in providing essential nutrients for breastfeeding mothers and their babies.
Dairy products such as yogurt and cheese are rich in calcium, important for bone health in lactating women. Greek yogurt, in particular, stands out for its higher protein content compared to regular yogurt, making it a favorable choice for breastfeeding moms.
While almonds and sesame seeds serve as non-dairy sources of calcium, dairy products remain a primary and convenient way to guarantee an adequate intake of this essential mineral for both maternal and infant bone development and maintenance.
Including dairy or suitable alternatives in the diet can greatly benefit the health of both the mother and the baby during the breastfeeding period.
Nuts and Seeds
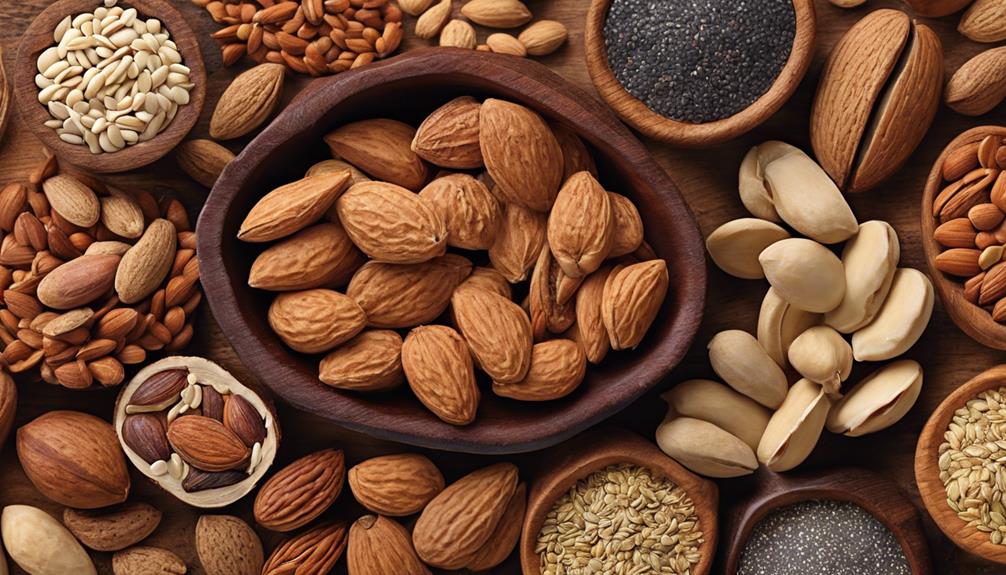

Nuts and seeds, being excellent sources of essential nutrients, play a vital role in supporting the dietary needs of breastfeeding mothers and their babies. Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and pumpkin seeds are great options to incorporate into a breastfeeding diet. These nutrient-dense foods help in maintaining energy levels, supporting brain function, and aiding in postpartum recovery.
Including a variety of nuts and seeds in our diet can provide a wide range of health benefits for both the mother and the baby. They're rich in protein, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals vital for breastfeeding moms. By easily adding nuts and seeds to meals, snacks, or smoothies, we can boost our nutritional intake during breastfeeding. These small but powerful foods offer a convenient way to enhance our diet and ensure we're meeting our dietary requirements during this important stage of motherhood.
Legumes and Beans
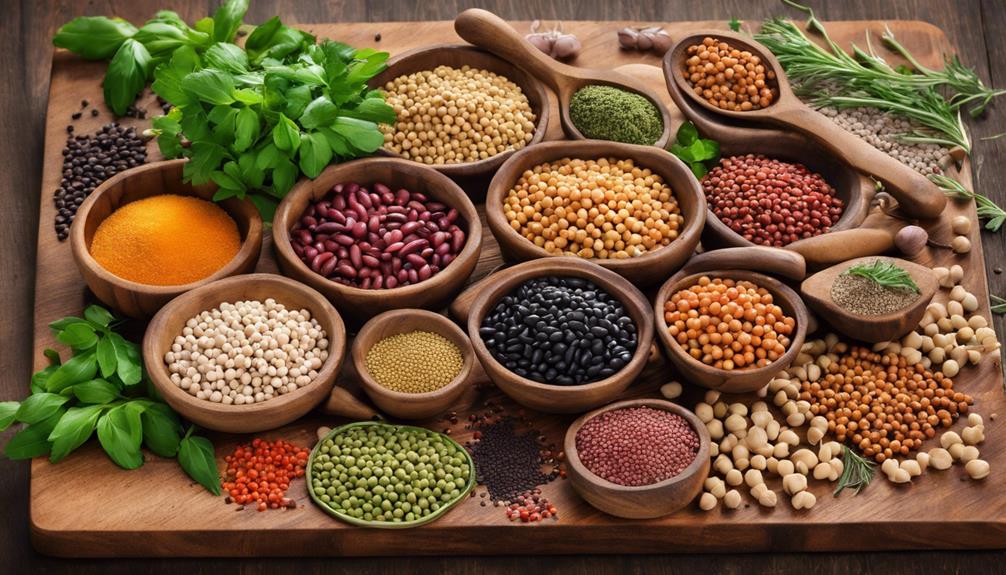

Legumes and beans, being excellent plant-based sources of protein, play an essential role in supporting the energy and muscle repair needs of breastfeeding mothers. These nutrient powerhouses aren't only rich in protein but also contain significant amounts of iron, a critical nutrient for maintaining energy levels and preventing fatigue in breastfeeding women. Additionally, legumes and beans provide fiber, minerals, and phytochemicals that support a robust immune system and help regulate hormones during the postpartum period.
Including legumes and beans in your daily diet can have numerous benefits for both you and your baby. The iron content in these foods can help prevent iron deficiency anemia, a common issue for new mothers. Furthermore, the fiber in legumes aids in digestion and can contribute to a feeling of fullness, which may be particularly beneficial when trying to meet the increased energy demands of breastfeeding. By incorporating legumes and beans into your meals, you can enhance the nutritional quality of your diet and support your overall well-being while nourishing your little one.
Healthy Fats

Incorporating a variety of healthy fats into our diet is essential for supporting brain development in breastfeeding babies and hormone production in mothers. These fats play a critical role in ensuring the well-being of both the mother and the baby during the breastfeeding journey.
Here are some key healthy fats to include in your diet:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids**: Found in fish and flaxseeds, omega-3 fatty acids are essential for brain development in infants and can contribute to improved cognitive function.
- Monounsaturated Fats: Avocados and nuts are rich sources of monounsaturated fats, vital for hormone production and nutrient absorption in breastfeeding moms. These fats also help in maintaining skin health and hormone balance.
- Medium-Chain Triglycerides**: Coconut oil contains medium-chain triglycerides, which offer a quick source of energy and may support postpartum weight loss efforts. Incorporating these healthy fats can boost energy levels and promote overall well-being for both mother and baby.
Hydration Essentials

Staying hydrated while breastfeeding is vital for both the mother's health and milk production. Monitoring urine color and scent can provide insights into hydration levels.
Adequate water intake is essential to support the body's functions and maintain an effective breastfeeding routine.
Importance of Hydration
Ensuring adequate hydration is essential for both milk production and maintaining a healthy breastfeeding relationship for mothers and babies. When it comes to breastfeeding, water is your best friend.
Here are some tips to keep you hydrated:
- Carry a reusable water bottle with you throughout the day.
- Set reminders on your phone to drink water regularly.
- Infuse water with fruits or herbs for an invigorating twist.
Best Hydration Practices
To maintain peak hydration levels during breastfeeding, it's important to prioritize consistent water intake throughout the day. Since breast milk is composed of 87% water, staying well-hydrated is vital for both the mother and baby.
Monitoring hydration can be done by paying attention to urine color and smell, with pale yellow urine indicating adequate hydration. Breastfeeding can increase thirst, attributed to oxytocin release, emphasizing the need to drink water to satisfy this thirst.
Best hydration supports milk production and overall health. Therefore, drinking water regularly throughout the day is essential for breastfeeding mothers to make sure they're adequately hydrated and able to provide their baby with the necessary fluids through breast milk.
Hydration for Breastfeeding
Adequate hydration plays a significant role in supporting breastfeeding mothers' milk production and overall health. Staying well-hydrated is essential for the best breastfeeding outcomes.
Here are some hydration essentials to keep in mind:
- Drink Water Regularly: Sip on water throughout the day and especially when feeling thirsty to maintain hydration levels.
- Aim for 8 Cups Daily: Consuming around 8 cups of water daily can help breastfeeding mothers stay adequately hydrated.
- Monitor Urine Color: Pay attention to the color of your urine; a pale yellow color indicates good hydration, while dark yellow may signal the need to increase fluid intake.
Ensuring proper hydration not only supports milk production but also helps prevent issues like constipation and fatigue commonly experienced by breastfeeding mothers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Should a Breastfeeding Mother Eat to Make Baby Healthy?
To make our baby healthy, we prioritize a diet rich in nutrient-dense foods like fish, meat, poultry, fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and fiber-rich starches. Including protein from lean meat, eggs, dairy, beans, and seafood supports growth and development.
What Are the Top 5 Foods to Eat While Breastfeeding?
We prioritize a balanced diet that includes salmon, leafy greens, sweet potatoes, Greek yogurt, and almonds for breastfeeding. These foods boost brain development, promote maternal health, and support bone strength. Our focus is on nourishing both mom and baby.
What Are the Guidelines for a Healthy Diet When Breastfeeding?
Staying nourished while breastfeeding involves eating a balanced diet with plenty of water, avoiding excessive caffeine and alcohol, and considering a postnatal vitamin. Tuning into hunger cues supports energy and milk production, ensuring both mom and baby thrive.
What Is a Healthy Breastfeeding Menu?
We focus on a balanced diet for breastfeeding, incorporating lean proteins, whole grains, colorful fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Our choices support our nutritional needs and promote health for both the baby and me during this critical time.
Conclusion
To sum up, maintaining a breastfeeding safe diet is essential for the health of both mom and baby. By incorporating nutrient-dense foods like leafy green vegetables and healthy fats, mothers can guarantee top-notch nutrition and energy levels while supporting milk production.
Remember, a well-balanced diet is key to a healthy and happy breastfeeding journey for both you and your little one. Make the right food choices for a thriving mom and baby duo!
With a rich background in writing and a keen interest in child development, she specializes in creating insightful, compassionate content that speaks directly to parents’ concerns and aspirations. Margaret believes in the power of shared experiences to bring comfort and confidence to parents everywhere.
-

 Third Trimester1 month ago
Third Trimester1 month agoManaging Nausea in the Third Trimester: A How-To Guide
-

 Third Trimester1 month ago
Third Trimester1 month agoSafe Third Trimester Exercise Guide for Moms-to-Be
-

 Breastfeeding/Formula Feeding4 weeks ago
Breastfeeding/Formula Feeding4 weeks agoOvercoming Formula Feeding Guilt: 10 Ways to Feel Empowered
-

 Breastfeeding/Formula Feeding2 months ago
Breastfeeding/Formula Feeding2 months agoDairy-Free Breastfeeding Diet: A Comprehensive Guide
-

 First Trimester3 weeks ago
First Trimester3 weeks agoDramamine Use in Pregnancy: First Trimester Guide
-

 Newborn Care1 month ago
Newborn Care1 month agoEssential Newborn Care: A How-To Guide for Parents
-

 Newborn Care1 month ago
Newborn Care1 month agoNewborn Care Basics: A Step-by-Step Guide
-

 Third Trimester2 months ago
Third Trimester2 months agoWhat Causes Low Platelets in Pregnancy During the Third Trimester?













