Prenatal tests help you understand your baby’s health and development early in pregnancy. Common tests include genetic screenings like non-invasive blood tests that detect conditions such as Down syndrome, and ultrasound scans to check fetal growth, anatomy, and heartbeat. These procedures are safe and provide valuable insights for your healthcare provider. If you want to learn more about each test and what to expect, keep exploring the details below.
Key Takeaways
- Genetic screening detects potential genetic conditions early in pregnancy through non-invasive blood tests.
- Ultrasound scans, like the nuchal translucency and anatomy scans, monitor fetal development and detect abnormalities.
- Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) analyzes fetal DNA in maternal blood with high accuracy.
- These tests provide essential information to guide healthcare decisions and ensure fetal health.
- Common prenatal tests are safe, painless, and typically performed between the 10th and 22nd weeks of pregnancy.
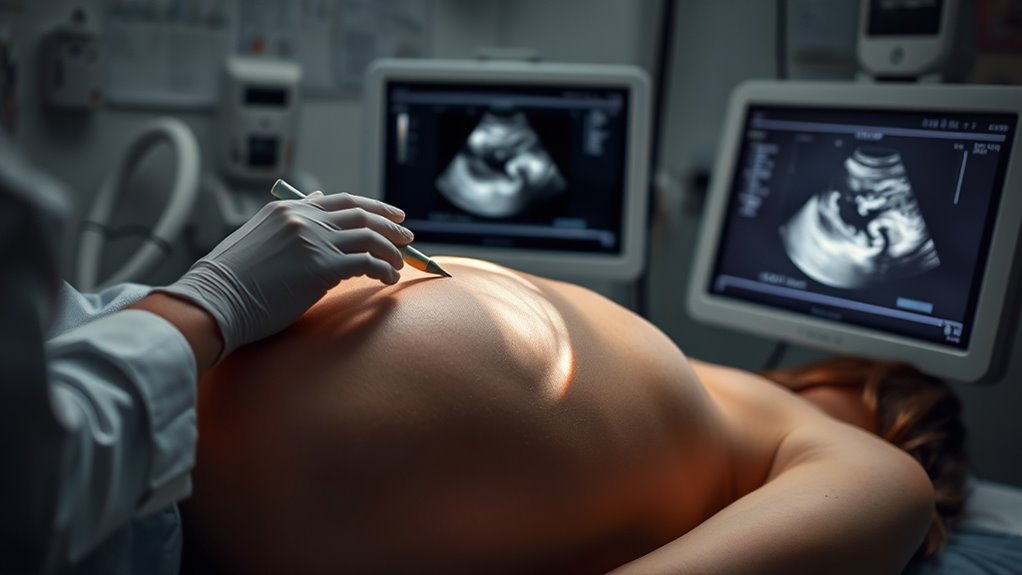
Are you curious about how doctors check the health of your developing baby? One of the first steps is usually genetic screening, which helps identify potential genetic conditions or abnormalities early on. These screenings often involve a simple blood test combined with a detailed ultrasound scan. The ultrasound scan uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of your baby inside the womb, giving your healthcare provider a clear view of growth, movement, and physical development. It’s a non-invasive way to monitor your baby’s progress and detect any potential issues.
Genetic screening is typically offered around the 10th to 14th week of pregnancy. It can detect conditions like Down syndrome, trisomy 18, and other chromosomal abnormalities. The process involves analyzing small amounts of fetal DNA present in your blood, which can provide important information about your baby’s genetic health without posing any risk to you or your baby. Some women also opt for additional screening tests, like the combined first-trimester screening, which combines blood tests and ultrasound measurements, or the non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT), which is highly accurate in detecting certain genetic conditions.
Genetic screening around 10–14 weeks detects chromosomal conditions safely through blood analysis.
Ultrasound scans are usually performed at various stages of pregnancy, with the most common being the nuchal translucency scan around 11 to 14 weeks and the detailed anatomy scan at 18 to 22 weeks. During these scans, your technician will move the transducer over your abdomen to capture images of your baby. The ultrasound provides crucial information, such as the baby’s heartbeat, movement, and position. It also measures the size of the fetus, ensuring proper growth, and checks the placenta’s location. This imaging can reveal potential issues like fluid buildup, structural abnormalities, or signs of miscarriage risk.
Additionally, advancements in neurological aspects of dreaming continue to shed light on how subconscious processing influences dream content, which may someday inform interpretations of prophetic dreams.
While genetic screening offers insights into your baby’s genetic makeup, ultrasound scans give you a visual confirmation of physical development. Together, these tests provide an all-encompassing picture of your baby’s health, helping your healthcare provider recommend any necessary follow-up or interventions. They’re both safe and essential tools to keep you informed and prepared throughout your pregnancy.
Understanding these tests can ease your worries and help you feel more involved in the health of your baby. Remember, your medical team is there to guide you through each step, explaining what each test shows and addressing any concerns you might have. Whether it’s a quick ultrasound or detailed genetic screening, these procedures serve as important milestones in ensuring your pregnancy progresses smoothly and your baby develops healthily.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Prenatal Tests Safe for the Baby?
Prenatal tests are generally safe for your baby, with fetal safety prioritized by healthcare providers. While testing offers valuable insights, keep in mind testing limitations, such as false positives or negatives, which can occur. You should discuss any concerns with your doctor to understand the risks and benefits. Overall, most prenatal tests pose minimal risk and help guarantee your baby’s health during pregnancy.
When Should I Schedule My First Prenatal Test?
You should schedule your first prenatal test around 8 to 12 weeks of pregnancy. Statistically, most women have their initial appointment within this window to guarantee early detection of potential issues. Timing considerations are vital for accurate results and effective planning. Early test scheduling helps you stay on top of your pregnancy health, allowing for timely interventions if needed. Don’t delay—book your appointment early for peace of mind.
Can I Refuse a Specific Prenatal Test?
Yes, you can refuse a specific prenatal test. Your choices are guided by ethical considerations and patient autonomy, meaning you have the right to make informed decisions about your healthcare. Before refusing, discuss your concerns with your healthcare provider to understand the purpose and implications of the test. Remember, it’s your body and your baby, and you’re entitled to make choices that align with your values and comfort level.
How Accurate Are Prenatal Screening Tests?
Prenatal screening tests are quite accurate, but their screening accuracy varies depending on the specific test. They generally have low false positive rates, meaning most positive results are true positives. However, no screening is perfect, so some false positives can occur. It is crucial to follow up with diagnostic tests for definitive answers. You should discuss the screening accuracy and false positive rates with your healthcare provider to understand the implications fully.
Do Prenatal Tests Detect All Genetic Conditions?
Prenatal tests can’t detect all genetic disorders because of test limitations. While they identify many conditions, some genetic disorders may go unnoticed, especially if they’re rare or result from new mutations. You should understand that no test is perfect, and false negatives or positives are possible. Discuss your concerns with your healthcare provider to get a clear picture of what tests can and can’t reveal about your baby’s genetic health.
Conclusion
Now that you know about these common prenatal tests, you’re better prepared to make informed choices for your pregnancy. Remember, just like a trusty compass guides a sailor, these tests help steer you toward a healthy journey ahead. Stay curious, ask questions, and trust your instincts—after all, this is your adventure. With the right knowledge, you’ll navigate this exciting time with confidence, ensuring the best start for your little one, no matter what the future holds.









